Every blockchain uses a specific consensus algorithm to secure itself from malicious attacks. This makes a consensus algorithm the most important part of any Blockchain network. It ensures that all transactions in a blockchain goes through a verification process by majority of the participants. This process keeps the records accurate and immutable.
What is a Consensus Algorithm?
A consensus algorithm refers to the methods through which peers participating in a Blockchain network reach an agreement among themselves. This agreement is crucial for determining what records should be on the Blockchain and what should not. It is also important in deciding improvements for the Blockchain.
The term consensus is synonymous with agreement, alignment and togetherness. It gives participants confidence in the Blockchain processes. It also ensures the security, reliability and stability of the network.
A consensus algorithm equally ensures that every block that successfully enters the Blockchain is authentic. It must be the one and only version of the truth notable to every participant in the network.
Objectives of a Consensus Algorithm
There are about 4 things a consensus algorithm seeks to achieve:
1. Reaching Agreement among participating parties (called nodes). No record can enter the Blockchain unless everyone participating in the network agrees that it is the only true record. 51% of members must be in alignment for this to happen. Otherwise, the record will not be viable.
2. Collaboration and Cooperation. Participants are required to work together to ensure the Blockchain is secure and efficient. Those who fail to cooperate face some form of penalty. This can be in the form of loss of stakes, denial of rewards or expulsion from the network.
3. Equal rights for all participants. Each member of the network possesses the same rights as all the others in the network. They can all have the full or part of the Blockchain records without restrictions.
4. Mandatory participation in consensus process. All participants are required to stay in sync with the Blockchain network processes. Those who stay offline more than is allowable may have to forfeit their stake in the network.
Types of Consensus Algorithms
We have several types of Blockchain Consensus Algorithms. For example, we have the Proof of Work, the Proof of Stake, the Proof of Burn, the Proof of Capacity, the Proof of Elapsed Time and many other consensus algorithms.
The two most popular algorithms are the Proof of Work (PoW) and the Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithms. In this piece, I will try to help you understand how the Proof of Work consensus algorithm works.
Proof of Work Consensus Algorithm
This is the consensus algorithm that the Bitcoin network and the original Ethereum network uses. It involves participants constantly trying to solve complex mathematical puzzles to provide an accurate solution. These puzzles require a lot of computational power.
Being the first to solve a puzzle successfully qualifies a participant to mine the next block that will go into the Blockchain. Whoever this is takes the rewards for that new block.
The process involving the use of the Proof of Work consensus algorithm is called mining. Verifying transactions in a new block; organizing them in the order they occurred within the block; and announcing this new block to the entire peer-to-peer network takes a little amount of time and energy.
However, the process of trying to solve the mathematical puzzles makes the whole thing hard and energy consuming. This difficulty ensures that the latest block is properly put next to the last block in the correct and up-to-date Blockchain.
The nodes (participants) who solve these puzzles get rewarded with some new cryptocurrency and the transaction fees for records in that block. Their new block is broadcast to all members of the network at the same time. This is for proper verification before adding to the Blockchain. All miners thus update their own copies of the Blockchain to stay in sync.
As more miners join the PoW algorithm, the difficulty in solving this mathematical puzzles increases. This ensures that the time it takes to find a block remains about the same always. For the Bitcoin network, it takes about 10mins to get one block and add it to the Blockchain!
Securing a PoW Consensus Algorithm
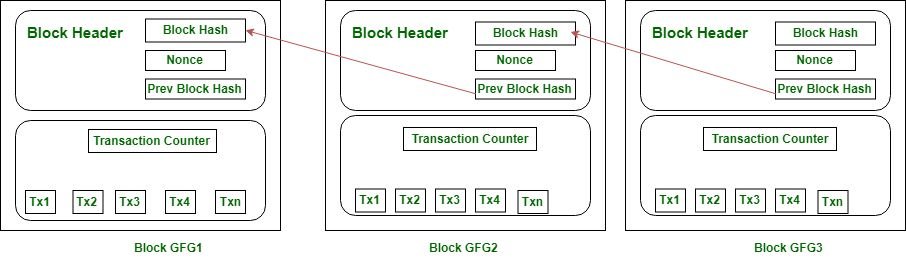
Take a look at this image above. (Source: https://geeksforgeeks.org)
Do you notice that the first block in the image, Block GFG1 has a connection with the one next to it, Block GFG2? This one in turn has a connection with the one following it, Block GFG3.
Every new block in the Blockchain contains a unique identifier called block hash. This is like a fingerprint that identifies the block, but instead of lines as with our fingers, they are made up of numbers and letters. Each new block carries the hash number of the block before it. This goes all the way down to the Genesis Block (the first block in the Blockchain) which has no previous block hash.
If anyone tries to alter the information in a block, they will only start to regenerate all the other blocks in the entire database all over again. No one can really pull this off successfully. It amounts to redoing all the computational work already done! Thus, the network will simply reject the block with fake information in it.
This keeps the Blockchain safe from the influence of bad network participants.
Two Significant Features of the PoW Consensus Algorithm
1. It is very hard to solve the mathematical puzzle that will grant a miner power to mine a block. This consumes so much energy while requiring huge computational power from miners. It is mostly miners with bigger computational power that gets the greatest chance to mine new blocks.
2. Once a solution is found by a miner, it is broadcast to the entire network. The validity of the new block found is very easy to verify as to whether it is correct. All the other miners has to verify this block before it becomes a part of the blockchian.
Advantages of Proof of Work
Here are some important things that makes PoW a favorite consensus algorithm for many:
1. It offers a uniquely EFFICIENT way to achieve consensus among participating parties while preventing abuse and misuse of the Blockchain.
2. It keeps the Blockchain truly DECENTRALIZED, eliminating the need for centralized institutional control of the Blockchain.
3. There is no single server for hackers to attack. Miners are scattered all over the world. This eliminates the possibility of a SINGLE POINT OF FAILURE.
4. PoW algorithm prevents bad actors from altering information already recorded in the Blockchain as well as stops them from adding malicious records to the database. Makes its blockchain IMMUTABLE.
5. It keeps transaction records authentic and traceable. Information on the PoW are TAMPER PROOF.
6. It is practically SAFE from attacks and hacks due to the outrageous cost of embarking on such. Thus it is almost impossible to attack.
Disadvantages of Proof of Work
Here are the most noticeable issues with the PoW consensus algorithm:
1. The 51% attack: if there is an entity that owns more than half of the total computational power for mining a block, they can easily corrupt the Blockchain when and however they want. This is because they possess majority of the network consensus required to validate a block successfully.
However, this is very much difficult and practically impossible currently.
2. It can consume too much time. Solving a puzzle can take a lot of time due to the increasing difficulties. This may lead to higher cost of transaction. Sadly, this is the case with the Bitcoin blockchain.
3. It is very costly to run: The amount of computational power one needs to participate is huge. The energy you have to exert for this is much. Heavy hardware and larger space have to be put into place, and this can take up lots of capital too.
4. Confirming a transaction may take 10-60minutes due to network congestions. Thus, transactions may not be as instantaneous as most expect it to be. In fact, it may take minutes, hours, or days.
Conclusion
Proof of Work consensus algorithm promises to be the best for security, but the energy cost is alarming. Blockchains like Bitcoin have several layer 2 solutions to solve some of the network’s challenges. A notable solution for the Bitcoin network scalability issue is the lightening network.
Other examples of cryptocurrencies that use the Proof of Work consensus algorithm include Litecoin, Ethereum, Monero coin and Dogecoin. Though, Ethereum is switching over to the Proof of Stake algorithm in the nearest future. Whether this will solve most of the major issues it currently faces remains a question.
In the next lesson in this series, I will discuss the Proof of Stake consensus algorithm. Did you enjoy this piece? Do leave your thoughts in the comments section. I will love to read them.